Circle Theorem ClassNotes.ng
Circle Theorems A circle is a set of points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point, called the center. The center is often used to name the circle. -T This circle shown is described as circle T; OT. As always, when we introduce a new topic we have to define the things we wish to talk about.

GCSE circle theorem revision cards Circle Theorems, Circle Math, Matching Activity, Aqa, Math
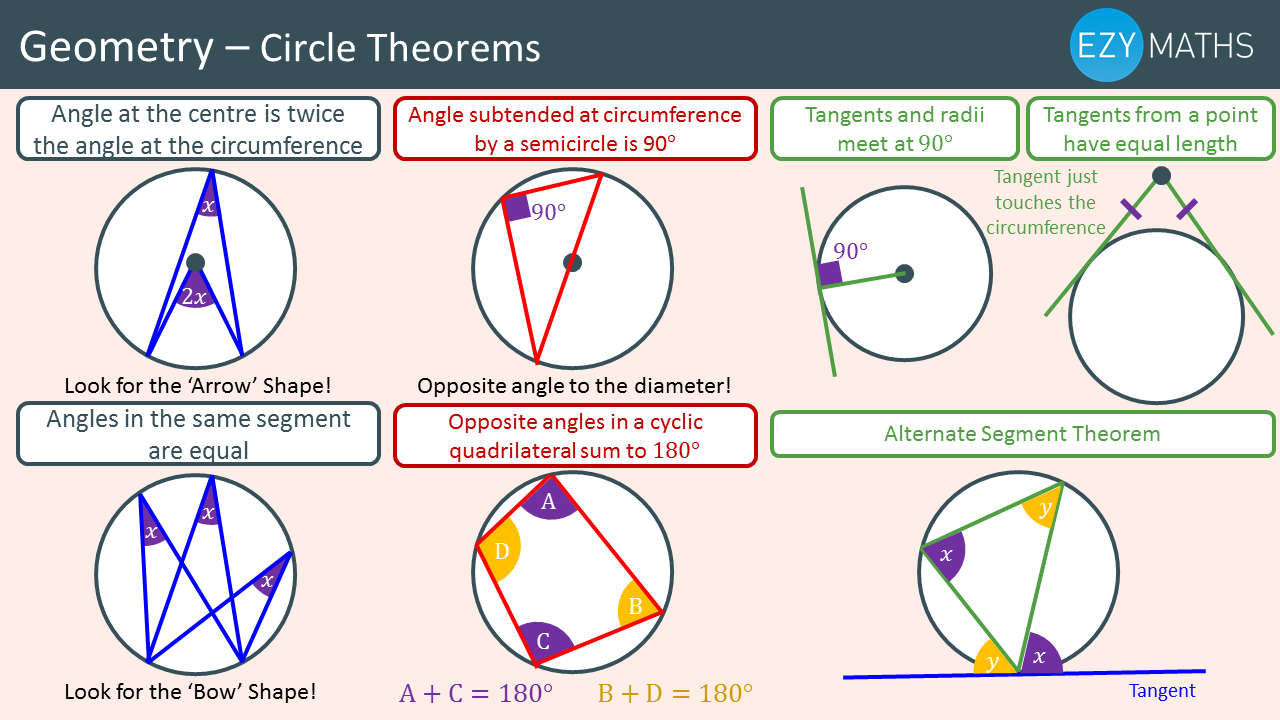
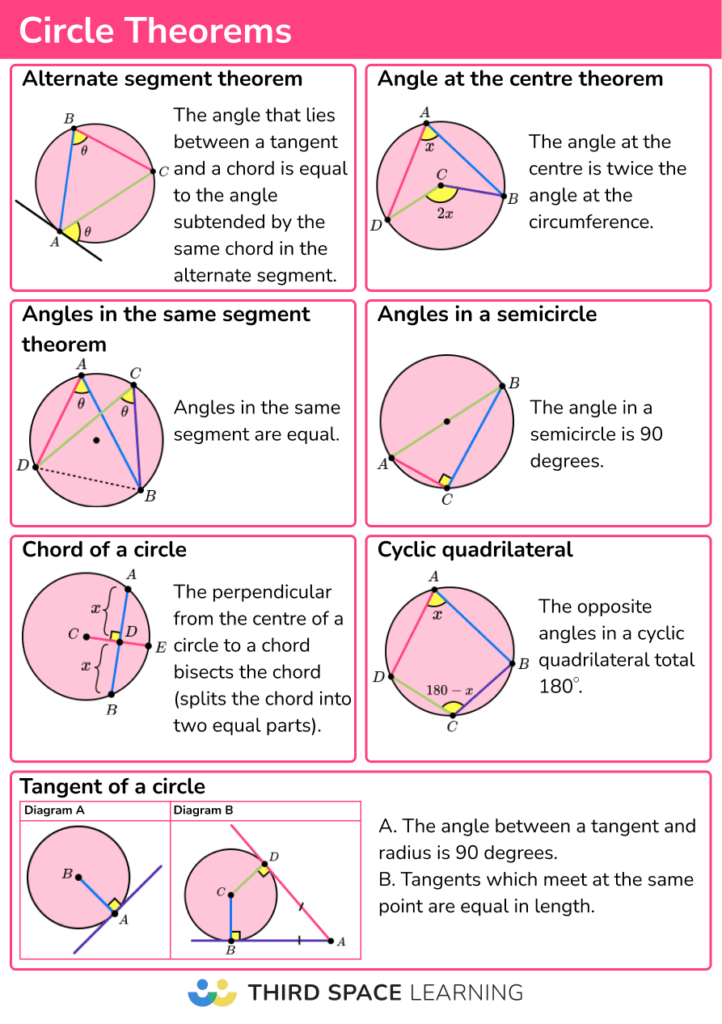
Circle Theorem 1: Angles at the centre and at the circumference The angle at the centre is twice the angle at the circumference. (Note that both angles are facing the same piece of arc, CB). Circle Theorem 2: Angle in a semicircle

more angles in a circle Circle theorems, Circle math, Math tutorials
There are seven circle theorems. An important word that is used in circle theorems is . Subtending An angle is created by two chords . The angle in between the two chords is subtended by.

️Gcse Maths Circle Theorems Worksheet Free Download Gambr.co
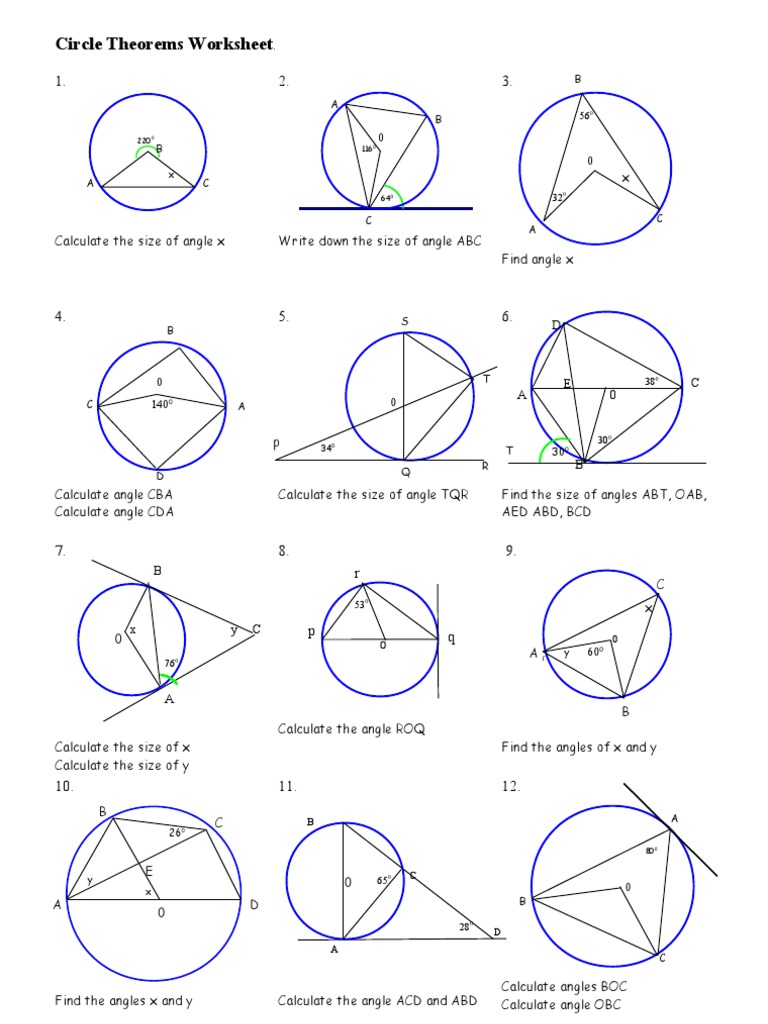
1.!(a) In the diagram below, O is the centre of the circle and A, B and C are points ! on the circumference.!Angle A = 29°!Work out the size of angle B.
Year 11 Maths Specialist Circle Theorems GeoGebra
Circle Theorems Theorems This section explains circle theorem, including tangents, sectors, angles and proofs. The video below highlights the rules you need to remember to work out circle theorems. Circle Theorem Watch on Isosceles Triangle Two Radii and a chord make an isosceles triangle. Perpendicular Chord Bisection

Free download Circle Theorem Flashcards and Matching Pairs Game Great Maths Teaching Ideas
Revision notes on Circle Theorems. Corbettmaths Videos, worksheets, 5-a-day and much more. Menu Skip to content.. Books; March 14, 2015 October 27, 2023 corbettmaths. Circle Theorems Notes Circle Theorems Revision. Circle Theorems pdf. Notes; Post navigation. Previous Worksheet Answers. Next Parts of the Circle Revision Notes. GCSE Revision.
️Circle Proofs Worksheet With Answers Free Download Qstion.co
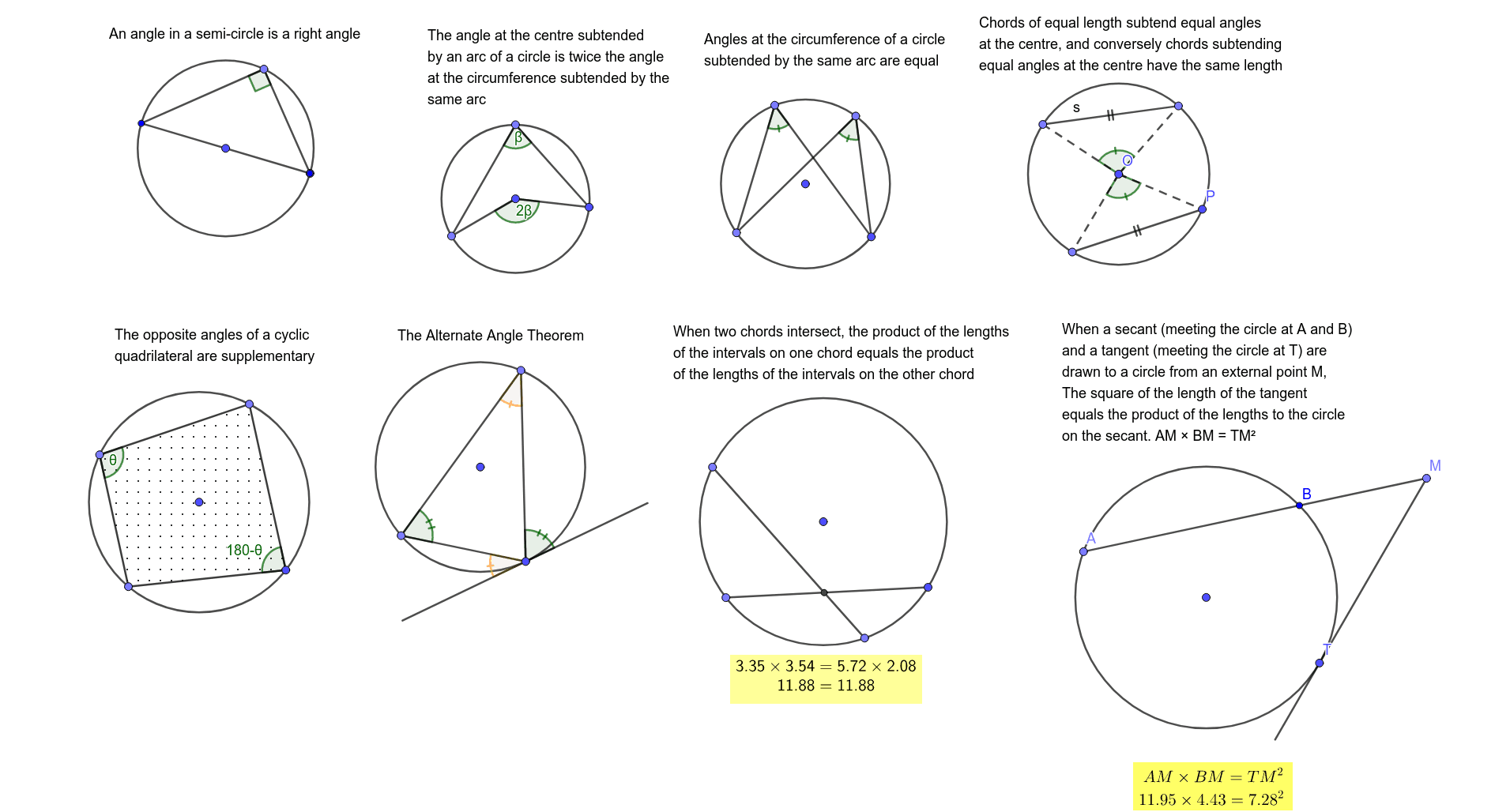
Theorem 1 The angle at the centre of a circle is twice the angle at the circumference subtended by the same arc. 375 P x° O 2x ° 376 Essential Advanced General Mathematics Proof Join points P and O and extend the line through O as shown in the diagram. Note that AO BO PO r the radius of the circle. Therefore = = = triangles PAO and PBO

Circle Theorems Gcse Worksheet
Proving circle theorems Angle in a semicircle We want to prove that the angle subtended at the circumference by a semicircle is a right angle. Step 1: Create the problem Draw a circle, mark its centre and draw a diameter through the centre. Use the diameter to form one side of a triangle. The other two sides should meet at a vertex somewhere on the
Equation Of A Circle Examples Outlet Shop, Save 61 jlcatj.gob.mx
Circle Theorems Videos 64/65 on Corbettmaths Question 2: Calculate the length of sides labelled in the circles below (a) (b) (c) Question 3: Calculate the length of sides labelled in the circles below (a) (b) (c) Question 4: Calculate the size of the missing angles (a) (b) (c)

Circle Theorems for GCSE and iGCSE. More information and maths revision on www.gcserevisionguide
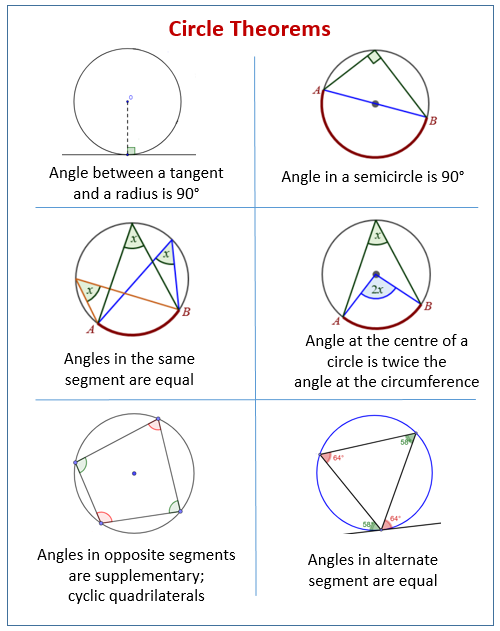
Circle Theorem 2 Opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral add up to 180°. =180−83=97° =180−92=88° Circle Theorem 3 The angle at the centre is twice the angle at the circumference. =104÷2=52° Circle Theorem 4 Angles in the same segment are equal. =42° =31° Circle Theorem 5 A tangent is perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact.

Circle TheoremsMaths Educational Wall Chart/Poster Amazon.co.uk Office Products
The points D, E and F are points on a circle, centre O. Angle DEF = Angle DOF = Angle EDO = Angle EFO is 14° smaller than angle DEF Work out the value of y. Circle Theorems pdf Created Date: 11/25/2019 1:51:26 PM.

Circle Theorems revision poster Teaching geometry, Math geometry, Circle theorems
A and B are points on the circumference of a circle, centre O. Angle ABO = 48° (i) Find the size of angle AOB. (ii) Give a reason for your answer. ° 5 (Total for Question 5 is 2 marks) A, B, C and D are points on the circumference of a circle. Angle BAD = 94° Angle ADC = 83° (i) Find the size of angle ABC. (ii) Give a reason for your answer.

Circle Theorems Poster Teaching Resources
5. Diagram NOT accurately drawn A and B are points on the circumference of a circle, centre O. PA and PB are tangents to the circle. Angle APB is 86°. Work out the size of the angle marked x. (3 marks) 6. R and S are two points on a circle, centre O. TS is a tangent to the circle. Angle RST = x. Prove that angle ROS = 2x. You must give reasons for each stage of your working.
Gcse Edexcel Maths Circle Theorems SexiezPicz Web Porn
Circle Theorems Angle at the centre The angle at the centre is twice the angle at the circumference (standing on the same chord). Angles in the same segment Angles at the circumference standing on the same chord and in the same segment are equal. Angle in a semicircle Angles at the circumference standing on a diameter are equal to 90o .

Circle Theorems Notes Corbettmaths
Circle Theorem 1: The alternate segment The angle that lies between a tangent and a chord is equal to the angle subtended by the same chord in the alternate segment. Step-by-step guide: Alternate segment theorem How to use the alternate segment theorem To use the alternate segment theorem Locate the key parts of the circle for the theorem.

Circle Theorems Bundle Teaching Resources
1. (a) In the diagram below, O is the centre of the circle and A, B and C are points on the circumference. Angle A = 29° Work out the size of angle B.